SLII® Training
Powering Inspired Leaders™
Use a situational leadership style to achieve success
The world’s most well-known leadership development course, SLII® Training, teaches managers how to forge deep bonds with their employees that have a multiplicative effect. Employee productivity and engagement increase when this occurs.
SLII® experience offers much more than just effective leadership development. Across the enterprise, it provides outstanding ROI.

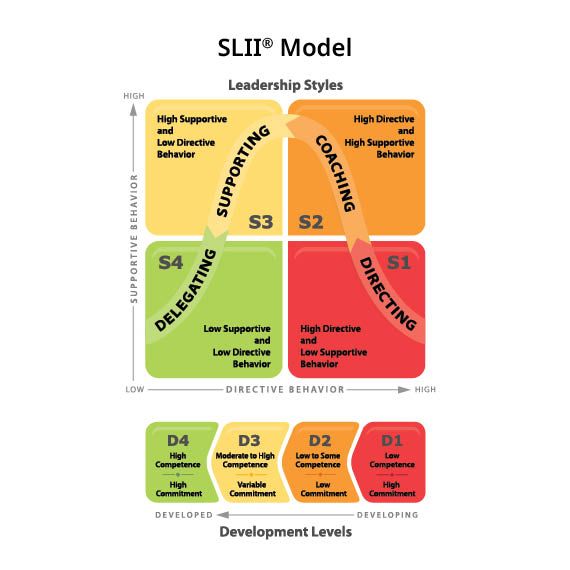
Proven, time-tested leadership model
SLII® is a practical, easy-to-understand framework to help your manager diagnose employee development for the following tasks: D1 – Enthusiastic Beginner; D2 – Disillusioned Learner; D3 – – Capable, but Cautious Contributor; D4 – Self-Reliant Achiever. Next, managers use appropriate support and coaching behaviors to help them succeed: S1 – Directing; S2 – Coaching; S3 – Supporting; S4 – Delegating.
Our award-winning learning program, The SLII Experience™, combines Blanchard’s latest research and cutting-edge design theory. This creates a learning experience that enables rapid mastery of the method and allows managers to help their direct reports reach new professional heights.
The Right Delivery Options for You
With thousands of qualified facilitators available worldwide, we can give your managers The SLII Experience™ in person or virtually, or we can train your trainers to deliver the course through public or private Training for Trainers courses.
To ensure that your managers can learn the methodology wherever they are and whenever they have the time, SLII® can also be a component of a learning journey or taught in a self-directed online or moderated online version.
The SLII® in-person experience is a 2-day, 8-hour course that uses a four-part learning path to ensure participants master the content and become situational leaders. Live in-person training offers the fullest content and the richest opportunities to practice new behaviors.
LAUNCH— participating in prework assignments, including assessments, accelerates
LEARN— Events teach leaders the skills and language to lead situationally and provide opportunities for one-on-one interaction with participants. (seven hours, including a 45-minute lunch break)
Practice— Leaders build new skills and practice their SLII® vocabulary in activities based on individual job challenges. They learn to match their leadership style and practice SLII® conversations. (9 hours, including a 45-minute lunch break)
Application— Tools and resources are available after the course to help participants strengthen and maintain their SLII® skills.
1 Day Instructor-led Course The SLII® in-person one-day experience uses the same four-part learning route but is eight hours long and more compacted. LAUNCH— To jumpstart the learning process and prepare participants’ minds for real-world problems, participants complete fun prework projects that include assessments.
LEARN— Activities give leaders the abilities and vocabulary to lead in various contexts.
PRACTISE— Activities based on one’s own professional issues help one learn new abilities.
APPLY— Tools and resources available after the workshops to aid participants in honing and maintaining their SLII® skills.
Virtual Instructor-led Course
The SLII® Virtual course consists of five live, two-hour virtual sessions* spread out over a few days. The virtual sessions give learners a fun learning environment incorporating group activities, instruction, and chances to put new abilities to use.
LAUNCH— Prework assignments and assessments help participants organize their thoughts before class.
LEARN (Sessions 1 & 2)— Activities teach leaders the abilities and terminology to lead in various situations.
PRACTISE (Sessions 3, 4, & 5)— In activities focused on their own professional problems, leaders build and practice their SLII® vocabulary.
APPLY— tools and resources to advance and maintain their SLII® skills.
*There is also a shortened option that consists of three 90-minute sessions.
Online Course with Collaboration
The SLII® Collaborative Online Experiences enable participants to learn from their peers and securely hone their abilities through a combination of live weekly sessions conducted by Blanchard experienced facilitators and moderators and asynchronous learning. Cohort-based sessions are spread out over a period of 5 weeks and combine self-directed learning on a cutting-edge platform that encourages interaction through conversations, exercises, reflection, and offline
Online Program
SLII® Online is a self-paced, on-demand training that teaches managers the fundamental ideas of SLII® and gives them conceptual practice. Optional can be added for more practice. The SLII® Online program is a three-hour online course divided into bite-sized modules lasting anywhere from one to twenty minutes. Optional debriefs that promote conversation and cooperation for a blended learning experience are also available. Contains interactive exercises: entertaining, captivating activities range from online discussions to films, games, stories, and case studies.
Online Overview
A self-paced, on-demand course called SLII® Overview introduces the technology while highlighting its key concepts through videos of fundamental material. This 35-minute online overview offers exposure to the key concepts of SLII®. It includes engaging micro-learning activities, videos, games, and worksheets.
SLII® Challenge Simulation
An immersive, simulation-focused experience on Advantexe designed to reinforce, practice, and apply the SLII® framework. Following a series of simulated dialogues, participants select the appropriate response for each circumstance. To show learners the effects of their decisions, scenarios are evaluated against the best practice behavior set for that particular scenario.
Digital kbassets
Our digital kbassets include tools, interactions, and micro-learning movies offering browseable information for just-in-time assistance.
Through digital kbassets, leaders can access adaptable micro-activities such as films, interactions, and worksheets to provide ongoing learning, performance support, reinforcement, and personalized learning journeys.

Great leaders make meaningful connections
Great leaders give employees what they need when needed. It means having authentic conversations to empower. Follow their development. Be their champion. See their commitment.
Leading situationally is very different from previous management styles. And this approach yields significantly higher returns than other management styles.
54%
of leaders use only one leadership style, regardless of the situation.*
50%
of the time, leaders use the wrong style to meet their people's needs.
Give your leaders the tools to motivate and accelerate performance
The current pace of change is so disruptive it requires visionary leadership. Managers need a leadership training program to prepare them to be agile situational leaders and empower their employees to succeed
Research Driven
Building on more than 30 years of leadership and desire research, SLII® incorporates the latest advances in neuroscience and evolves with the ever-changing workplace.
Proven Results
More than 10,000 companies use SLII® to increase productivity, reduce sales, and increase sales and profits.
Develop Inspiring Leaders
SLII® addresses the need for competence, empowerment, and brain engagement by creating a safe workplace where employees can problem-solve, innovate, and collaborate.
Universally Effective
SLII® is relevant to global leaders, regardless of industry, language, or job role. SLII® teaches leaders to give the right direction or support their people at the right time.
SLII® training enables leaders to build deeper
relationships
With more inspired leaders, morale and cohesion will improve, team members will feel supported, and employees will become more creative and productive problem solvers.
SLII® helps managers accelerate the development of their direct reports, from enthusiastic beginners to self-sufficient entrepreneurs.
When managers and team members speak the same language, misunderstandings, micromanagement, and frustration disappear.
retention
Leaders who match their style to the needs of their employees improve morale, commitment, and engagement.
unlock
Research shows that employees who feel supported by their managers are more engaged, one of the cornerstones of innovation.
Ready to get started?
SLII® can be taught face-to-face, virtually, online, or as a combination of learning modes. Contact us today to learn how SLII® can empower your leaders to make meaningful connections that create exponential impact.
SLII® can be taught face-to-face, virtually, online, or as a combination of learning modes. Contact us today to learn how SLII® can empower your leaders to make meaningful connections that create exponential impact.

